📘 Scenario:
A DJ app manages multiple playlists like "House Classics" and "Chill Vibes". Internally, each playlist might use a different storage mechanism (like an array, ArrayList, or set), but the DJ simply wants to play through the songs one-by-one without worrying about how they’re stored.
⚠️ Problem:
- Each playlist uses a different data structure to store songs.
- The DJ app has to know internal details of every playlist type to loop through songs.
- This violates encapsulation and makes code harder to maintain or extend.
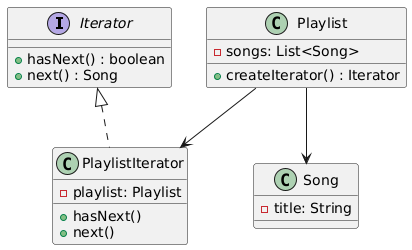
💡 Iterator Pattern Solution:
We define a common Iterator interface that provides methods like hasNext() and next().
Each playlist type implements this interface, allowing the DJ to step through songs uniformly—without needing to know how the playlist stores its data internally.
🖥️ Output:
=== DJ Playlist === Now playing: "Levels" by Avicii Now playing: "Strobe" by deadmau5